
JOIN US! TMS Education Event - Tuesday, April 9th 5:30pm pst - Click to learn more!
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
TMS for Traumatic Brain Injury
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is a complex medical condition resulting from a blow, jolt, or bump to the head that disrupts normal brain function. It's a major cause of death and disability worldwide, affecting millions each year. TBIs range from mild (commonly known as concussions) to severe, potentially leading to prolonged unconsciousness or amnesia.
TBIs can occur due to a range of events, such as falls, accidents, sports-related injuries, and aggressive attacks. The impact of TBI on an individual's life can be profound, affecting their ability to work, engage in social relationships, and perform daily activities. Furthermore, individuals who have had a traumatic brain injury have a higher chance of developing depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Study
Recovering from a Traumatic Brain Injury is a deeply personal and varied journey, as each individual's path to healing is unique. The process often involves a multidisciplinary approach, including physical therapy, occupational therapy, and cognitive rehabilitation to help regain lost skills and adapt to new ways of living. For many, recovery includes relearning basic tasks, such as walking and talking, and it can extend to more complex cognitive functions like memory, concentration, and problem-solving. Emotional and psychological support is also crucial, as coping with the changes brought on by a TBI can be challenging.The recovery process’s duration and severity differ according to the magnitude of the injury and the individual’s overall health status. However, with adequate time, patience, and proper support, considerable improvement can be achieved. TBI recovery aims to restore physical function and help individuals find new ways to engage with the world, rediscover their strengths, and achieve the best possible quality of life.
Why TMS for TBI?
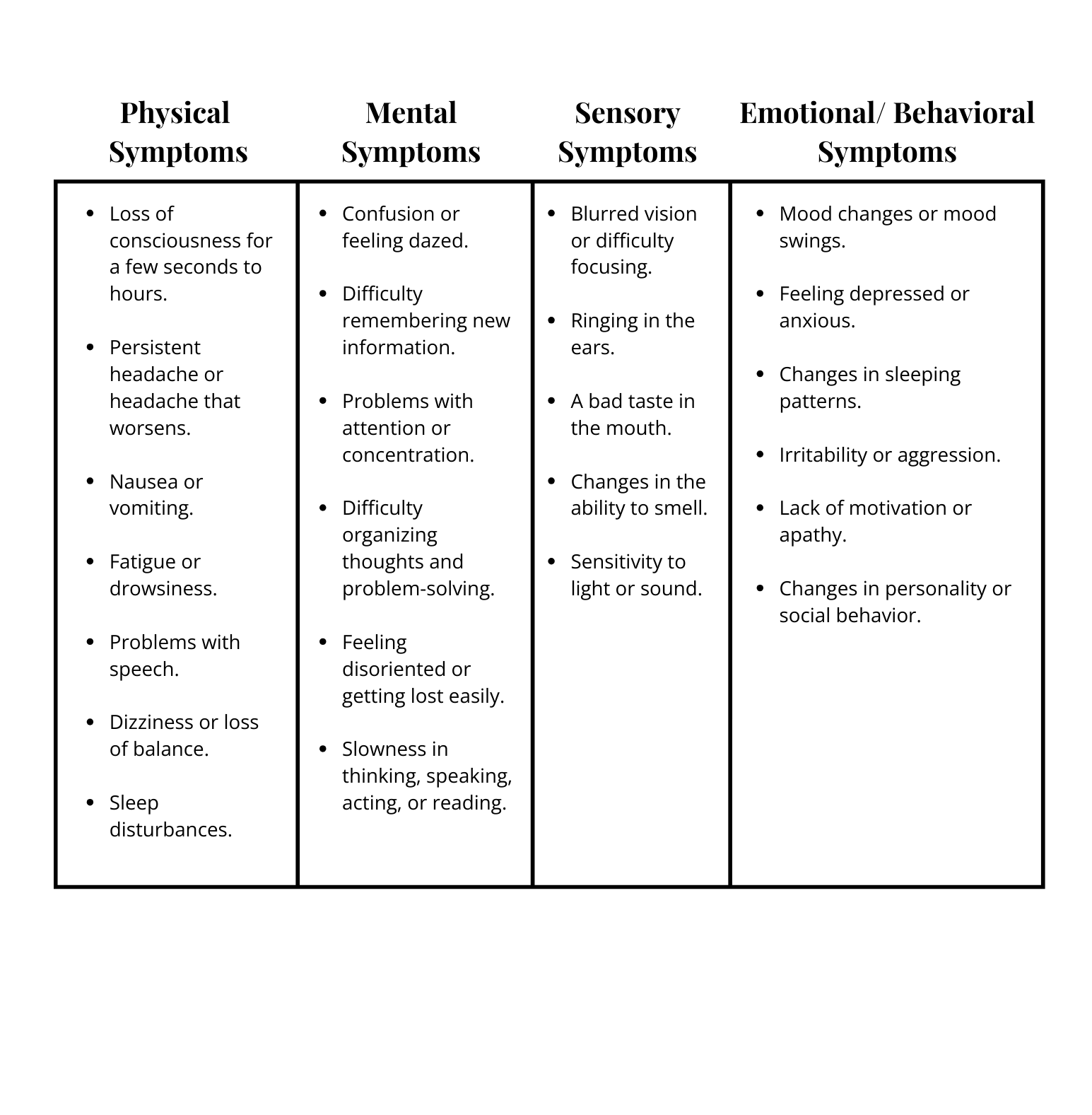
Common Symptoms:
The manifestations of TBI can differ greatly, influenced by the injury’s severity and the specific brain region impacted. They can be physical, sensory, cognitive, or emotional in nature. Symptoms might appear immediately after the traumatic event, or they may not manifest for days or weeks. Here are some of the most common symptoms across different categories:
How TMS Helps in the Rehabilitation Process:
- Neural Stimulation: TMS can stimulate or modulate neural activity in the brain regions affected by the injury, potentially leading to improved cognitive and motor function.
- Promoting Neuroplasticity: TMS might promote neuroplasticity, the brain's ability to form and reorganize synaptic connections, especially in times of injury and repair. This can help in the recovery of functions lost due to TBI.
- Reducing Symptoms of Depression and Anxiety: Individuals with TBI often experience secondary issues like depression or anxiety. TMS has been shown to be effective in treating these conditions, which can significantly improve quality of life.
- Cognitive Function Improvement: Some studies suggest that TMS may improve cognitive functions such as memory, attention, and executive function in individuals with TBI. By targeting specific brain regions associated with these cognitive processes, TMS could potentially enhance cognitive rehabilitation efforts.
- Pain Management: TBI patients often experience chronic pain, which can be debilitating. TMS has shown potential in pain management, possibly providing relief by modulating pain perception pathways in the brain.
- Customizable Treatment: TMS can be targeted to stimulate specific parts of the brain, depending on the individual's needs. This customization allows for a more personalized treatment approach, which is essential given the diverse nature of TBIs.
What patients are saying
"Desperate and struggling, my therapist recommended TMS. With an open mind and cautious optimism, I tried it. In just five days, my anxiety improved significantly. The clinic staff was fantastic, offering counseling and education on anxiety. The whole experience, including aftercare and follow-up, made a huge difference. I wholeheartedly recommend Accelerated TMS at Kind Health Group. Thank you, Dr. Nanos, and your amazing team"
Pink, A., Williams, C., Alderman, N., & Stoffels, M. (2019). The use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) following traumatic brain injury (TBI): A scoping review. Neuropsychological Rehabilitation, 30(10), 1914-1936. https://doi.org/10.1080/09602011.2019.1706585
Abstract: This scoping review explores the application of rTMS after TBI, focusing on its therapeutic efficacy for various sequelae. The review includes 30 empirical studies and suggests that rTMS has potential as a therapeutic intervention for multiple symptoms after TBI, including depression, dizziness, central pain, and visual neglect. However, the results are mixed for cognitive outcomes and less encouraging for prolonged disorders of consciousness. The review recommends more comprehensive guidelines and sufficient reporting of rTMS parameters and procedures.
Meek, B. P., Hill, S., & Modirrousta, M. (2020). Accelerated repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in the treatment of post-concussion symptoms due to mild traumatic brain injury: A pilot study. Brain Injury, 35(1), 58-65. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699052.2020.1857837
Abstract: This pilot study investigates the feasibility, tolerability, and efficacy of twice-daily, low-frequency rTMS over the right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in reducing chronic post-concussion symptoms in patients with mild TBI. The study observes significant improvements in overall post-concussion symptoms, disability, pain ratings, depression, and anxiety symptoms, as well as improvements in verbal fluency, working memory, selective attention, and cognitive processing speed.
If this is a life-threatening emergency, please call 911 or the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline














































